FREIGHT RAIL HAZMAT SAFETY KEY FACTS
- The hazmat accident rates per carload is at record lows, down 80% since 2005.
- Shippers provide compliant tank cars; railroads ensure safe routing and handling.
- 24/7 response teams, training, and AskRail help ensure safety.
👆 Check out an overview video from our new video series Harley Explains.
Railroads play a vital role in safely transporting hazardous materials essential to daily life, such as water purification chemicals and fertilizers. In collaboration with regulators and communities, they ensure secure deliveries under their common carrier obligation. By adhering to strict hazmat rail car design standards, developing first responder apps, and utilizing advanced routing software, railroads continuously enhance safety.
Thanks to ongoing investments, FRA data shows hazmat accident rates per carload have reached record lows—down 80% since 2005. Freight rail remains the safest way to transport hazmat, with more than 99.99% of shipments arriving without a release due to a train accident.
Important to Know: The overwhelming majority of all tank cars are owned or leased by shippers, not the railroads. Shippers have a responsibility to ensure they are using the appropriate tank cars and intermodal tanks for safe movement of their products before offering it to the railroads for shipment. Federal requirements allow the railroad to trust that the shipper has taken all appropriate measures unless a ground-level inspection suggests otherwise. If those requirements are met, railroads are required to move products under their common carrier obligation. Learn more on shipper regulatory responsibilities.
Complying with Federal Regulations
Railroads comply with federal regulations as well as industry-wide and railroad-specific operating procedures to ensure safe operations. Industry and railroad-specific procedures cover employee training, train speeds, inspections, rail yard practices and locomotive operation.
Federal regulations from various agencies, including the FRA and the Pipeline & Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA), dictate safety practices in areas such as placement of railcars carrying certain commodities in the train “consist,” hazmat routes, an inspection of equipment and track, speed restrictions and more. While federal regulations dictate the frequency of inspections, railroads often inspect their infrastructure with greater regularity than the federal government requires.
Private Investments Increase Safety
In 2023, Class I railroads reinvested $26.8 billion in modernizing infrastructure, enhancing safety and improving reliability. Using advanced technology—such as drones for inspections, ultrasound for track flaws, and trackside monitors for railcar defects—railroads proactively detect and address issues before incidents occur. Given the highly integrated rail network, railroads collaborate on industry-wide initiatives to share data, ensuring quick identification of potential equipment issues across multiple rail systems.
Advocating for Tougher Standards
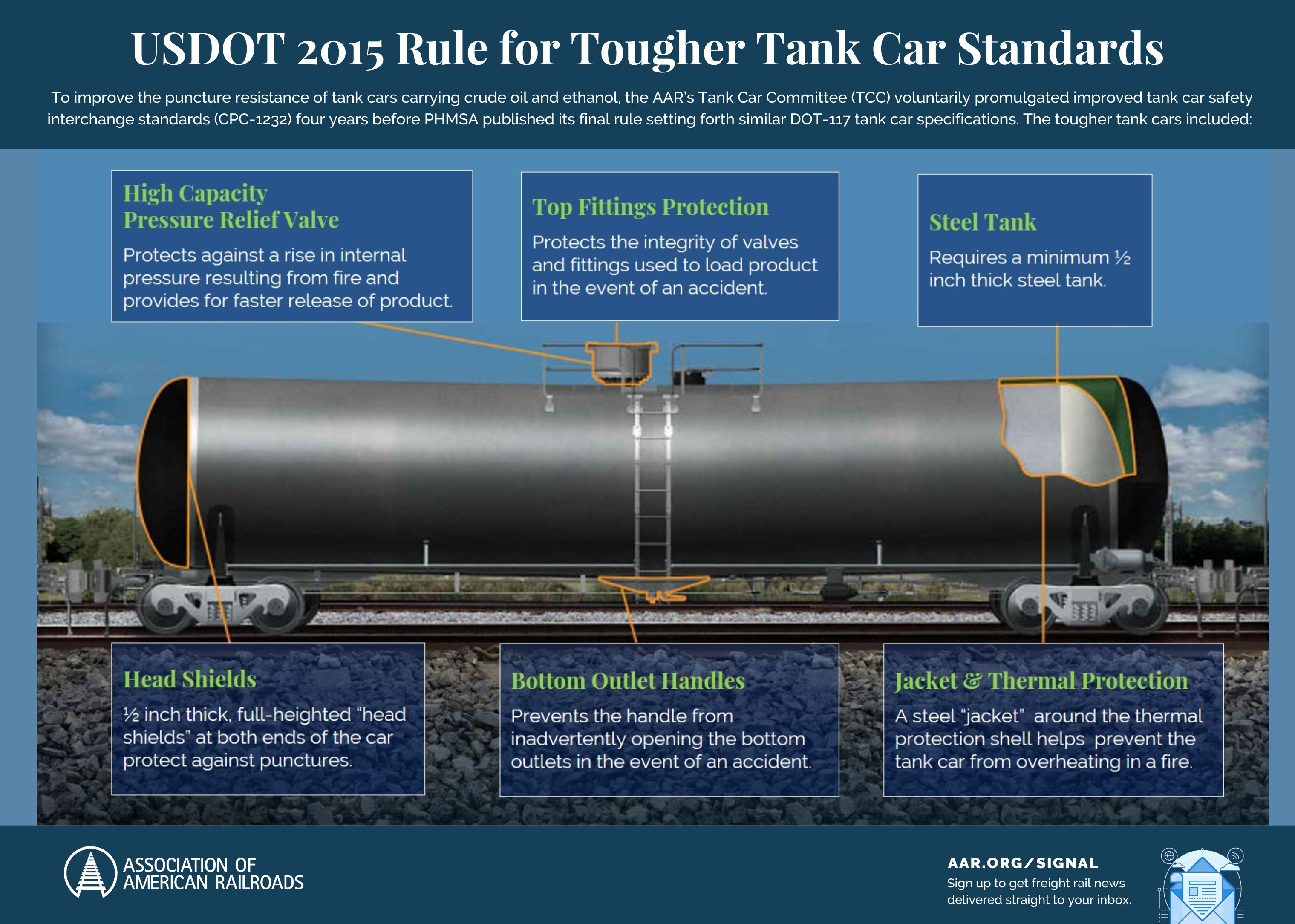
America’s freight railroads transport most hazmat using a fleet of specialized rail tank cars and have advocated for tougher standards. Thanks to rail industry advocacy, in 2015, USDOT released regulations requiring new, tougher tank car standards for certain types of hazmat, including crude oil. Older tank cars that do not meet new standards are being phased out. Railroads also proactively equip many trains carrying hazmat with equipment designed to enhance rail braking and minimize damage to rail cars in the event of an accident.
U.S. Class I railroads use the Rail Corridor Risk Management System (RCRMS), a joint initiative between railroads and the government, to analyze and identify the safest and most secure routes for transporting highly hazardous materials. The model uses 27 risk factors — including hazmat volume, trip length and population density along the route — to assess rail routes’ overall safety and security.
24/7 Emergency Response Teams
Along with always-on response teams that support local officials, railroads also maintain networks of on-call hazmat response contractors and environmental consultants to provide additional assistance. Freight railroads have a fundamental commitment to the safety of the communities they serve all across the country.
Working with government and industry partners like MxV Rail, railroads help train tens of thousands of emergency responders each year and actively collaborate with local officials on emergency response plans in the event of an incident. Emergency response agencies can, upon request, receive confidential information on the hazmat moving through their communities.
Emergency Response Plans
Railroads actively collaborate with local officials on emergency response plans. Upon request, railroads also share information with state and local officials on the types of cargo moving through their communities to inform emergency response planning. In partnership with the International Association of Fire Chiefs, the industry developed the AskRail app, which provides first responders across the rail network immediate access to accurate, timely data about what type of hazmat a rail car is carrying and how to respond to an incident safely.
Hazmat Remediation
Railroads follow strict regulations when a hazmat incident occurs. When a hazardous substance incident occurs, railroads work closely with government agencies and safety experts to immediately contain the situation, protect the health and safety of citizens and the environment, remediate any impacts and carefully return to service.
Railroads rigorously adhere to federal and state regulations for hazardous substance transportation, collaborating with regulatory agencies, deploying environmental experts, and actively engaging in monitoring and remediation to minimize hazmat incident impacts. Their commitment extends to supporting affected communities until resolution.